Hair restoration is a complex subspecialty that provides great relief to people suffering from hair loss. Since the original description, the approach to surgical hair restoration has been transformed by greater understanding of the aesthetics of hair loss and cosmetic hair restoration, hair anatomy and physiology, and the advent of micro vascular surgical instruments according to the best hair transplant clinic in India. Graft size, site construction, packing density, and medical control of hair loss are all factors that contribute to the present state of the art in hair restoration.
Hair
restoration produces natural-looking outcomes that are backed by a high level
of patient satisfaction and safety. This part of cosmetic surgery is a
fantastic source of internal cross-referral and is a welcome addition to a
typical aesthetic practise. Hair restoration surgery in the future will be
focussed on minimal-incision surgery and cell-based therapies.
Alopecia is a general term for hair loss that
involves a loss of visible hair. Alopecia comes in a variety of forms.
Androgenic alopecia is the most frequent type of surgically curable alopecia
(AGA). The existence of scalp hair has long been associated with traits of
health, energy, vitality, and strength. As a result, hair loss in males (MAGA,
or male pattern androgenic alopecia) and women (FPHL, or female pattern hair
loss) can have serious psychosocial consequences.
Hair
transplants account for the vast majority of hair restoration treatments, and
the introduction of microvascular surgical instruments, as well as a better
understanding of the anatomy and physiology of hair loss, has transformed the
art of surgical hair restoration since its inception.
Anatomy,
Genetics, and Physiology of Hair Loss:
In
genetically predisposed males and some women, androgenic alopecia is
characterised by increasing noticeable thinning of scalp hair. The latest
scientific evidence suggests that AGA is a polygenic characteristic. Variants
of the androgen receptor gene, which is found on the X chromosome, have been
linked to significant outcomes.
Caucasians
have the highest incidence of AGA, followed by Asians, Africans, and Native
Americans, with Native Americans having the lowest rate.The frontal, midscalp,
vertex, and temporal portions of the scalp can be split for hair
transplantation purposes. Hair thinning and shedding are caused by the gradual
shrinking of genetically marked hair follicles, which is characterised by a
reduction in the anagen (growth) phase of the hair follicle and an increase in
the telogen/anagen ratio of the affected scalp suggested by the best hair
transplant clinic in Kolkata. The
physiology of hair loss is inextricably tied to an understanding of the typical
hair follicle life cycle.
Although
testosterone is the most common androgen that causes hair loss, it must first
be transformed to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by the enzyme 5-reductase in order
to be most effective. The absence of AGA in men with congenital impairment of
type II 5-reductase and varied amounts of hair regrowth in men with MAGA
treated with finasteride, a selective type II 5-reductase inhibitor,
demonstrate the relevance of DHT as an etiologic factor in male pattern hair
loss. Excessive amounts of 5-reductase, DHT, and the DHT androgen receptor are
found in the balding scalp. DHT's activity is mediated by nuclear androgen
receptors found within cells.
There
is no consensus among women on whether or not hair loss is actually androgen
dependent. The majority of FPHL patients do not have biochemical
hyperandrogenism. In fact, some women with no detectable circulating androgens
may acquire FPHL, implying that non-androgen-dependent processes may play a
role. Based on this information, it is reasonable to replace the term
androgenic alopecia in women with the more recent and scientifically
descriptive term female pattern hair loss (FPHL), which encompasses this known
variation.
The
bulk of human hair shafts come from the scalp in single-, two-, and three-hair
clusters on a macro level. The groups are the apparent surface of the
follicular unit, which is a separate histologic structure (FU). Follicular
units are almost solely used as the transferred element of tissue in today's
hair transplants, hence this operation is now known as a follicular unit hair
transplant (FUT).
Nonsurgical
Options for Treating Hair Loss:
Only
two drugs have been licenced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to
enhance scalp hair growth. Finasteride and minoxidil are the drugs in question.
Other drugs that claim to treat hair loss are many, but their effectiveness is
debatable.
Finasteride
(Propecia; Merck & Co, Inc, Whitehouse Station, New Jersey) is a medicine
that inhibits the 5-reductase type 2 pathways, lowering DHT levels. Finasteride
was proven to prevent hair loss or have favourable benefits related to hair
growth in 90% of patients in a prospective randomised study conducted by the
company, and independent research has also confirmed the drug's safety and
efficacy.
Propecia
is solely approved by the FDA for men. The FDA only authorises the company to
make claims about hair development in the vertex area of the scalp, although
many doctors have noticed that this medication has a broad effect on the hair
on the scalp.
Minoxidil (Rogaine; McNeil-PPC, Inc, Morris
Plains, New Jersey) has been available since 1988 as a topical medication
indicated to treat hair loss. It has been used in men and women. The mechanism
of action is unclear, but it is recognized that the vasodilatory effects of minoxidil
do not fully explain its positive action on hair growth. Observed benefits
include increased proliferation of dermal papillae cells, increased hair
caliber, and diminished telogen phase during the hair growth cycle.
Evaluation
and Planning:
The
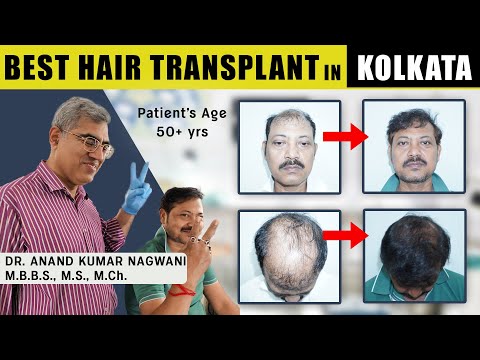
main metric by which results are objectively documented is photography of the
hair restoration surgery (HRS) result. Hair photography has been defined in
terms of lighting and typical positions. To avoid the upper borders of black
hair blending into the backdrop, a light grey or blue-colored background is
recommended. This background is also suitable for people with white or blond
hair.
General
Evaluation:
The
indicators of hair loss have been particularly distressing. Because of their
low self-esteem and vulnerability to an imagined outcome, this group of
patients is more prone to rash decisions and excessive expectations. For
patients with hair loss, managing these expectations and developing a realistic
surgical plan is important to the procedure's long-term success.
The
fact that hair loss is progressive is a critical idea that physicians and
patients should keep in mind when evaluating and preparing for HRS. Hair loss
that appears in the office during a consultation is only a snapshot in a
long-term process that began years ago and will continue till death.
Communication
on the quality of the patient's donor hair is also an important part of
managing expectations.Curl, hair shaft diameter, colour, texture, follicular
unit density, and the telogen/anogen ratio of in situ donor hair are all traits
that should be examined. These characteristics of the donor hair should be
examined and documented in order to anticipate how well the transplanted hair
would conceal scalp baldness according to the best hair
transplant surgeon in India.





No comments:
Post a Comment